WHERE NATURE MEETS THE SPIRIT
The historic church of Analipsi was originally built in 1886, near the “Cave of the Lakes” at Kastria. It is said that the church was found on a rock with the imprint of the Ascension of Virgin Mary. East of the church at close proximity, there is a small but impressive gorge with a waterfall.
Geodiversity
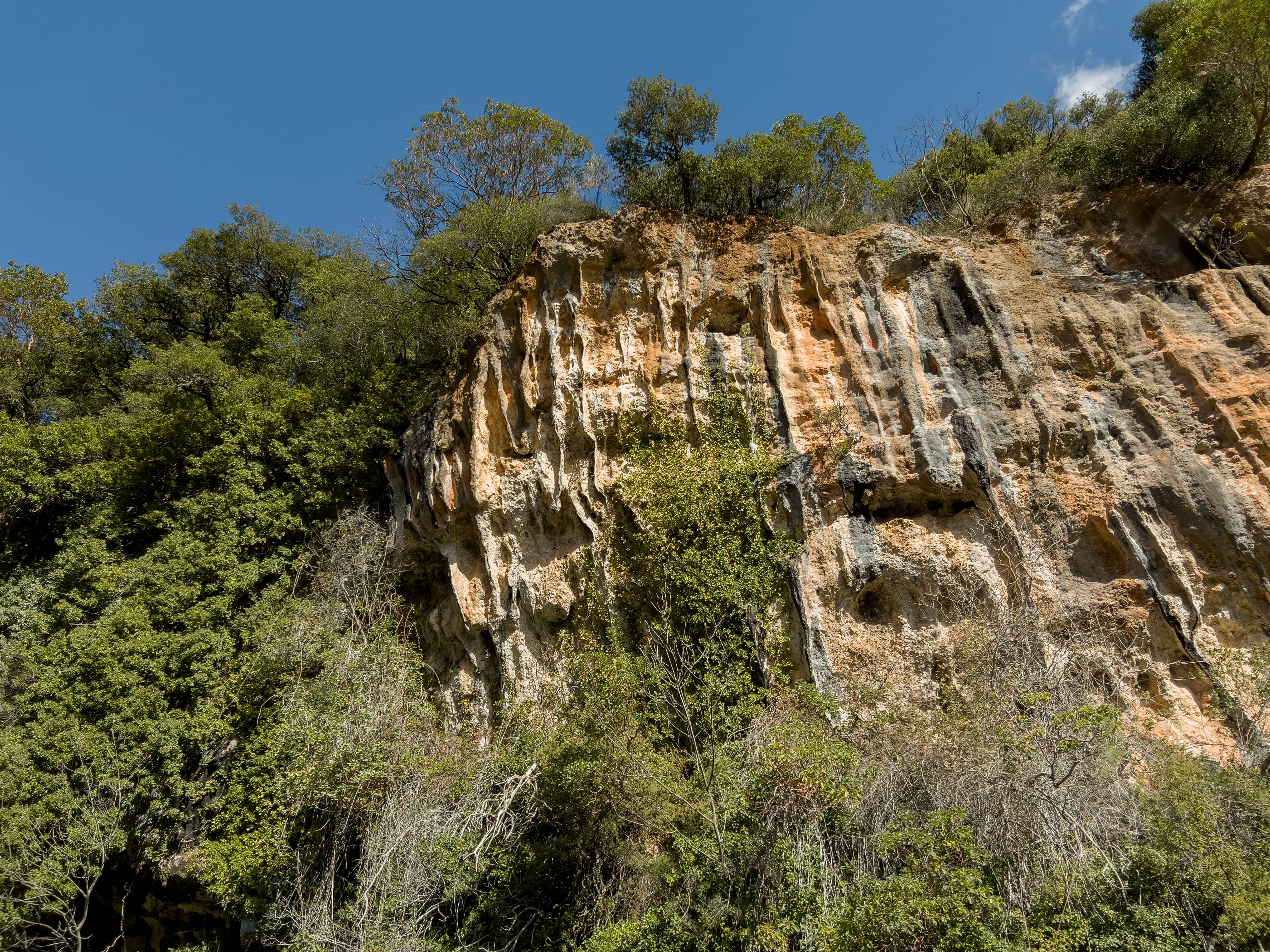
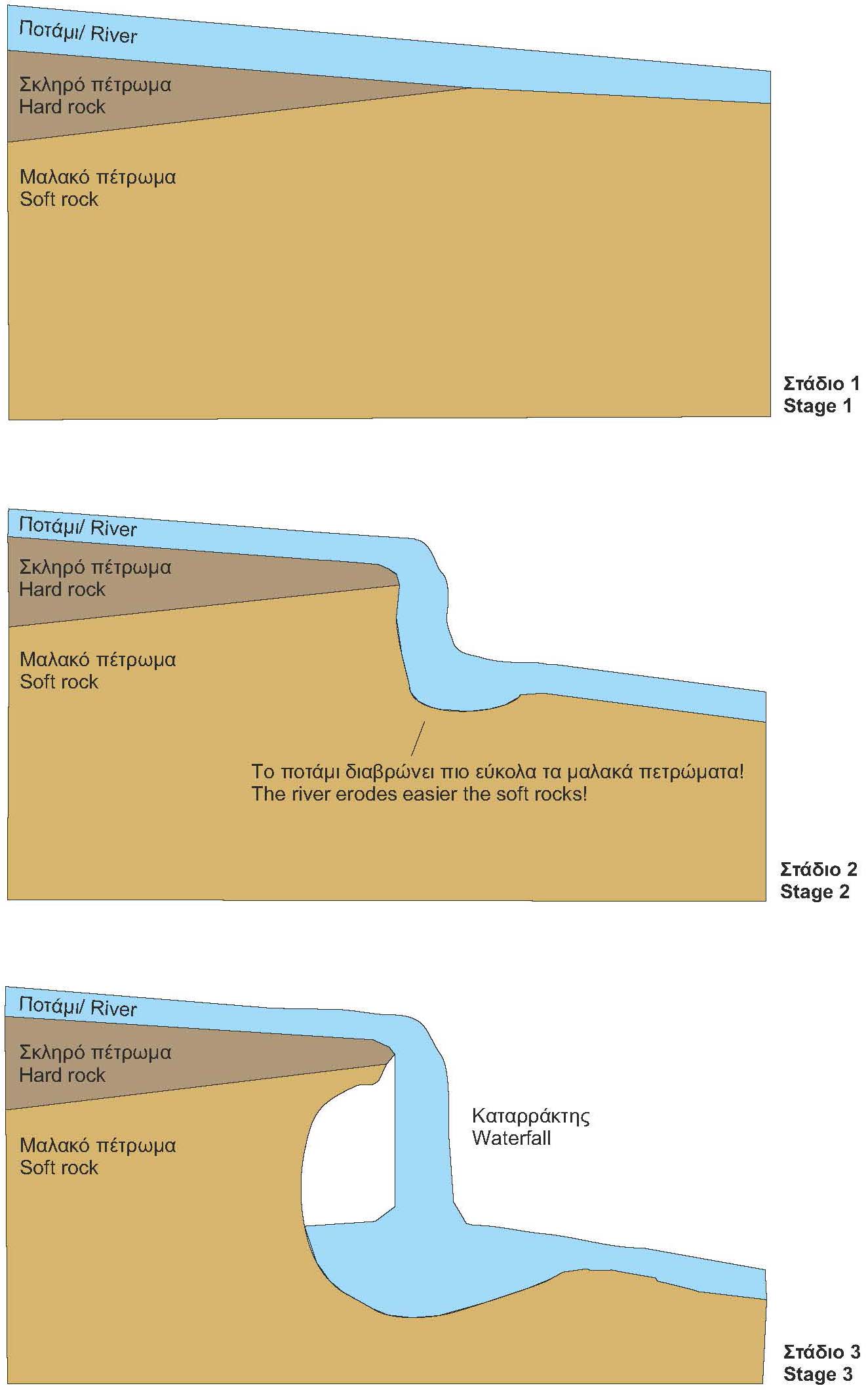
It consists part of a valley that was formed along a big fault between limestones of Tripolis Unit and radiolarites of Pindos Unit. Limestones are rocks that are easily eroded by the chemical action of water (karstification), while radiolarites are insoluble rocks eroded by mechanical erosion.
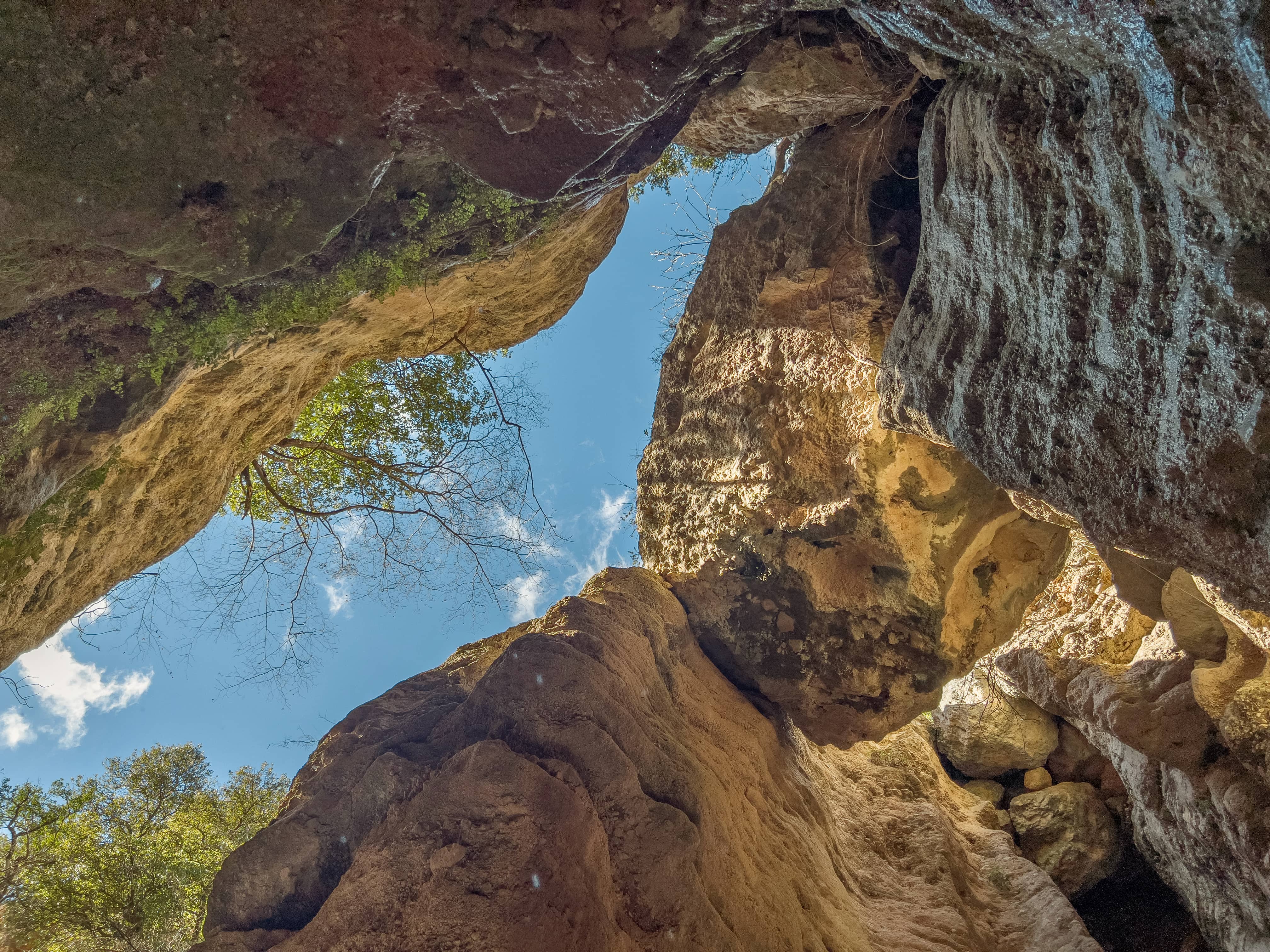
This river channel drained water from Chelmos Mt. towards the Polje of Lousoi. As the wider region was getting uplifted, the polje and the river channel were getting deeper due to intense erosion. Gradually, the sediments transported by the river were deposited and filled the valley around the former riverbed . Recently, a new river channel was formed, eroding vertically the previous deposits, forming the small but impressive gorge where a waterfall is flowing east of the chapel. As erosion progressed, this waterfall migrated gradually to the west. Today, we can track down the traces of the former positions of the waterfall east of the modern one.
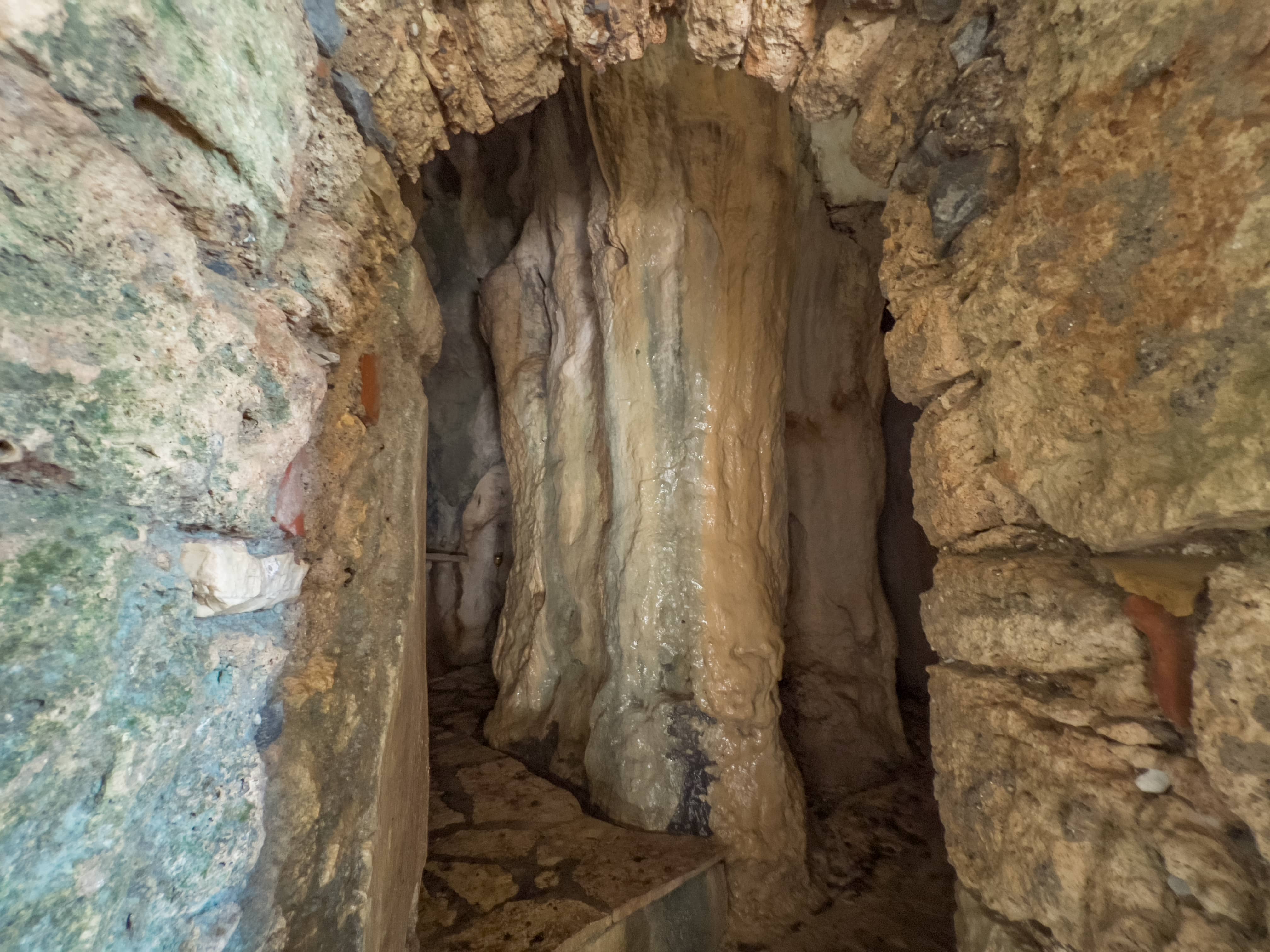
The dark limestones that appear on the western steep slope of the valley present intensive karstification. Also, due to karstification a small cavity was formed, with several speleothems. The interior of which today constitutes the sanctuary of the temple of the church of Analipsi.
Biodiversity
The Geosite is located within the Protected Area “SPILAIO KASTRION” (GR2320009) of the Natura 2000 network. Formations of evergreen broad-leaved species cover the majority of the area, with the dominant species being Quercus coccifera and Juniperus oxycedrus and phrygana communities with species such as Sarcopoterium spinosum and Phlomis fruticosa.
Rare plant species are found in the limestone rocks of the area, such as the Peloponnesian endemic Asperula arcadiensis, Greek endemics such as Centaurea raphanina subsp. mixta.
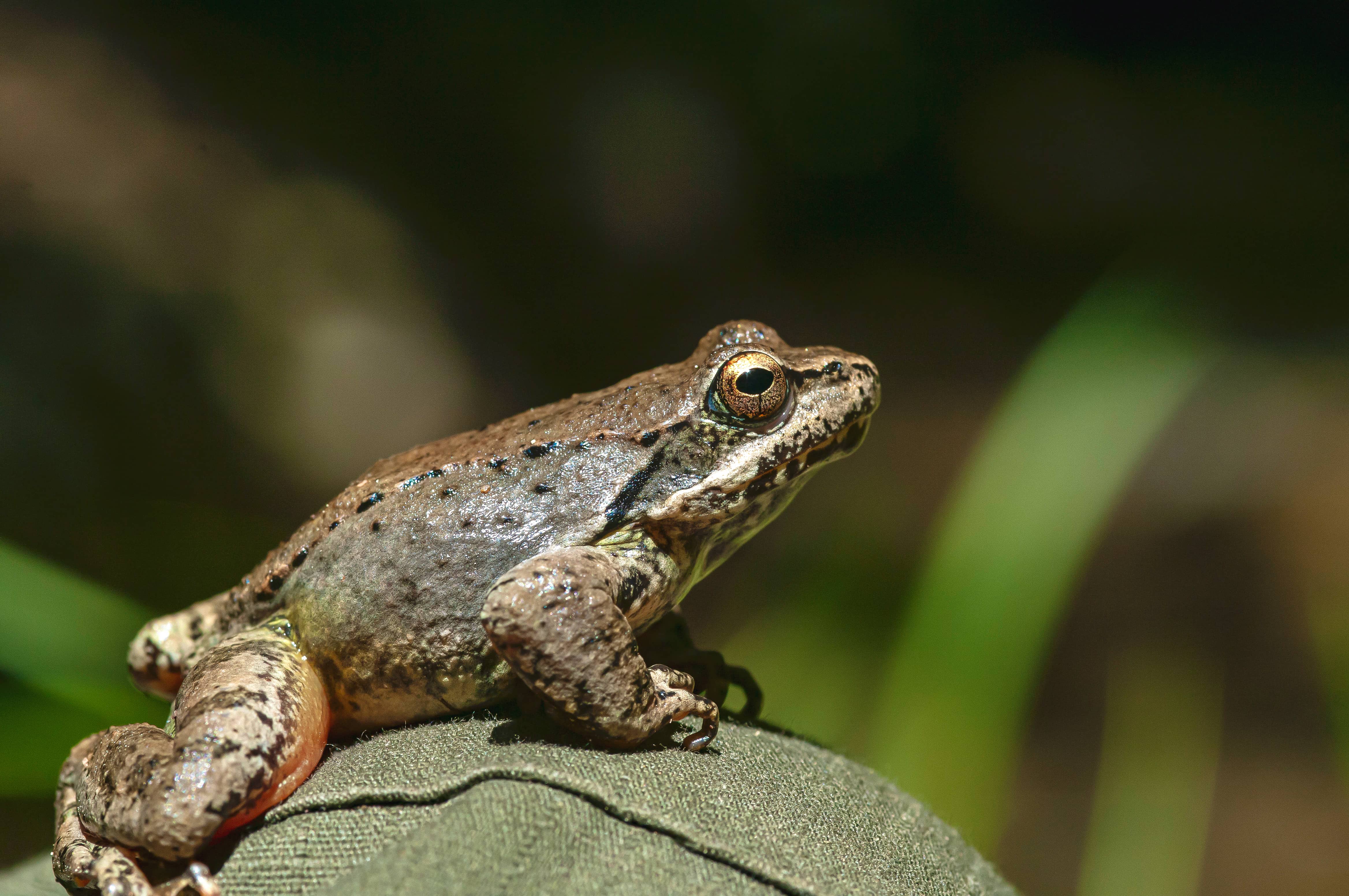
Important species of fauna recorded from the area are the Greek stream frog Rana graeca and the Peloponnesian wall lizard (Podarcis peloponnesiaca), an endemic lizard of Peloponnese.